How to Increase your Stem Cells Naturally 2024
If you search online for stem cell supplements, you’re bound to find a long list. Do stem cell supplements really work? Figuring out what to make of all of these supplements can be pretty daunting, as each claims to be the best and greatest.
What are stem cells?
Stem cells are a type of cell that has the potential to develop into different cell types in the body. Because of this, these types of cells can serve as a repair system and theoretically divide without limit to replenish other cells for as long as you are alive.In theory, the best scenario would be to increase the quantity of stem cells while we are young and then use them to keep our heart, joints, brain, and other parts of our body healthy as we age.
Stem Cells Develop Into All Cells, Renew Organs
We develop from stem cells. When the father’s sperm meets the mother’s egg, a fertilized egg is formed. It continues to divide and by day three to five develops into an embryo consisting of about 150 stem cells in the mother’s uterus. Later, these stem cells in the embryo continue to split and form various tissues and organs in the human body. There are more than two hundred different kinds of cells in the human body, all of which grow from stem cells.
Stem cells are not only present at the embryonic development stage. When babies are born, they carry a large number of stem cells within their bodies. The average person has about 37.2 trillion cells, including about 750 million stem cells, which account for 0.002 percent of the total cells (Page 27, Eat to Beat Disease). These stem cells are stored in various parts of the body, ready to regenerate or repair body tissues and organs.
Dr. William Li, the author of “Eat to Beat Disease,” president of the Angiogenesis Foundation and a Harvard-trained medical doctor, elaborated on the role of stem cells in an interview with The Epoch Times. Li said stem cells are mainly stored in the bone marrow, though also found in the body’s fat, skin, hair follicles, and even in the heart. He made an analogy: The human body retains and dispatches stem cells just like we keep unused paint in the garage during renovation, which is ready for use if necessary, say, for wall repair someday.
As all human tissues and organs get renewed constantly, stem cells play a key role in this process. Specifically, we need them to produce new skin to replace damaged skin cells; and to replace damaged cells on the surface of the intestine. Besides, hematopoietic stem cells divide and replace those blood cells that are damaged while operating in the circulatory system. They, too, evolve into types of white and red blood cells, and more.
Interestingly, our small intestine is renewed every two to four days; our lungs and stomach every eight days; our skin every two weeks; our red blood cells every four months; our fat cells every eight years; and our skeleton every ten years. Dr. Li cited an example: The body’s immune cells regenerate every seven days. Therefore, if a person’s relevant stem cells disappear, he or she could die soon from an infection (Page 26, “Eat to Beat Disease”).
In addition, he quoted a Japanese story of nuclear radiation to highlight the critical life-supporting role of stem cells in his book. During the Second World War, the atomic bombardments in the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki caused about 200,000 deaths. Afterward, a second wave of deaths hit certain survivors because the ability of their bone marrow to make stem cells had been destroyed due to exposure to radiation. Further, in cancer treatment, chemotherapy and radiotherapy affect the survival of stem cells while destroying cancer cells, putting patients in tremendous pain and challenges (page 26, “Eat to Beat Disease“).
Related: Best Stem Cell Supplements
How can we boost stem cells?
There are a few well-known methods for accessing stem cells that can be used for serious medical conditions and situations. These are considered stem cell-based therapies and are used in the specialty of regenerative medicine. Keep in mind that these strategies would not be used for just any health and wellness program but instead, under medical supervision and for a specific medical issue.The invasive methods (some more invasive than others) used to access stem cells in humans include:
- Bone marrow stores, which can be harvested by drilling into bone for a biopsy.
- Adipose/fat cells, which can be harvested by liposuction.
- Blood extraction by apheresis, a machine in blood banks that looks like a dialysis unit.
This important scientific finding in rodents fits well with the broader body of research that nutrition—or temporary absence thereof during fasting—has profound effects on the behavior of cells and the maintenance of health, even in humans.
The principal investigator on this seminal fasting/stem cell study in mice, Ömer H. Yilmaz, M.D., Ph.D., shared the possible future implications on his research, that "fasting has many effects in the intestine, which included boosting regeneration as well as potential uses in any type of ailment that impinges on the intestine, such as infections or cancers."
Although mice may show changes in stem cell function after just 24 hours, in humans, studies indicate prolonged fasts (several days) may be used to trigger stem-cell-based regeneration that rejuvenates the immune system. This hopeful idea was studied by the team at University of Southern California led by Valter D. Longo, Ph.D., and initial results were published in 2014.
Using two to four days of a fasting-mimicking diet (FMD) in patients undergoing chemotherapy for various cancer diagnoses, patients experienced protection from the toxicity of treatments. The study has profound implications for promoting healthier aging processes, as immune cell function and protection from disease declines with age.
Using fasting (something our ancestors regularly practiced, due to food scarcity) to theoretically kill older and damaged intestinal cells or immune cells and replacing them with stem-cell-derived new ones opens doors to regenerative biohacking. In other words, a practical lifestyle method to make your stem cells work for you. In the words of Longo: "We could not predict that prolonged fasting would have such a remarkable effect in promoting stem-cell-based regeneration."
Can we all use fasting to augment stem cells or regenerative processes?
Although not directly increasing stem cells (like the rodent studies elegantly demonstrate), a pivotal and rigorously designed randomized, controlled cross-over trial research published in 2017, does demonstrate cellular clean-up and regeneration following fasting.The study included 100 healthy individuals; 71 ultimately completed a fasting-mimicking diet (FMD) regimen (800 to 1,100 calories daily of a plant-based diet low in protein and simple carbohydrates that is commercially available) for five consecutive days a month for three months in a row. In contrast, the control group consumed an unrestricted diet every day.
Compared with the control group, the intervention group following the prolonged "fast" experienced a reduction in body weight, abdominal fat, blood pressure, fasting glucose, lipids (total and LDL cholesterol), inflammation (C-reactive protein), and a tumor marker called IGF-1. The FMD results were so compelling, Longo and colleagues received a patent.
This important clinical trial demonstrated safety of the FMD and efficacy in reducing key biomarkers (risk factors) involved in aging, metabolic health, and chronic disease. The clinical trial results were so compelling, Longo and colleagues received a patent.
More research on FMD and intermittent fasting is currently underway in humans and has produced regenerative and even anti-aging results10 across a variety of patient groups. Fasting has been shown to positively affect:
Other Natural Ways to Activate Stem Cells
So we know that fasting can help stimulate stem cell production (definitely in mice; more to come from human studies), that raises the question: Are there are any other natural activators of stem cells?In addition to a healthful diet and physical activity, certain foods and supplements may support stem cell health too.
Foods that Activate Stem Cells
There is a growing amount of data that show phytochemicals (specifically polyphenols) confer antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that protect and benefit stem cells.
There are thousands of unique polyphenols. The best-studied ones for stem cell benefits include resveratrol, curcumin, quercetin, EGCG, genistein, daidzein, caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, kaempferol, and piceatannol. The mechanisms from this preclinical research has definite potential for positive implications in cancer, cardiovascular, and neurocognitive disease processes, to name a few.
Dr. William Li gives advice on how to protect the activity of stem cells in the body and actively mobilize them to repair the body from a dietary perspective. Human experiments have confirmed the following foods, which can increase the number of stem cells.
1. Olive oil
PubMed has indexed 30 research studies on olive oil and stem cell.
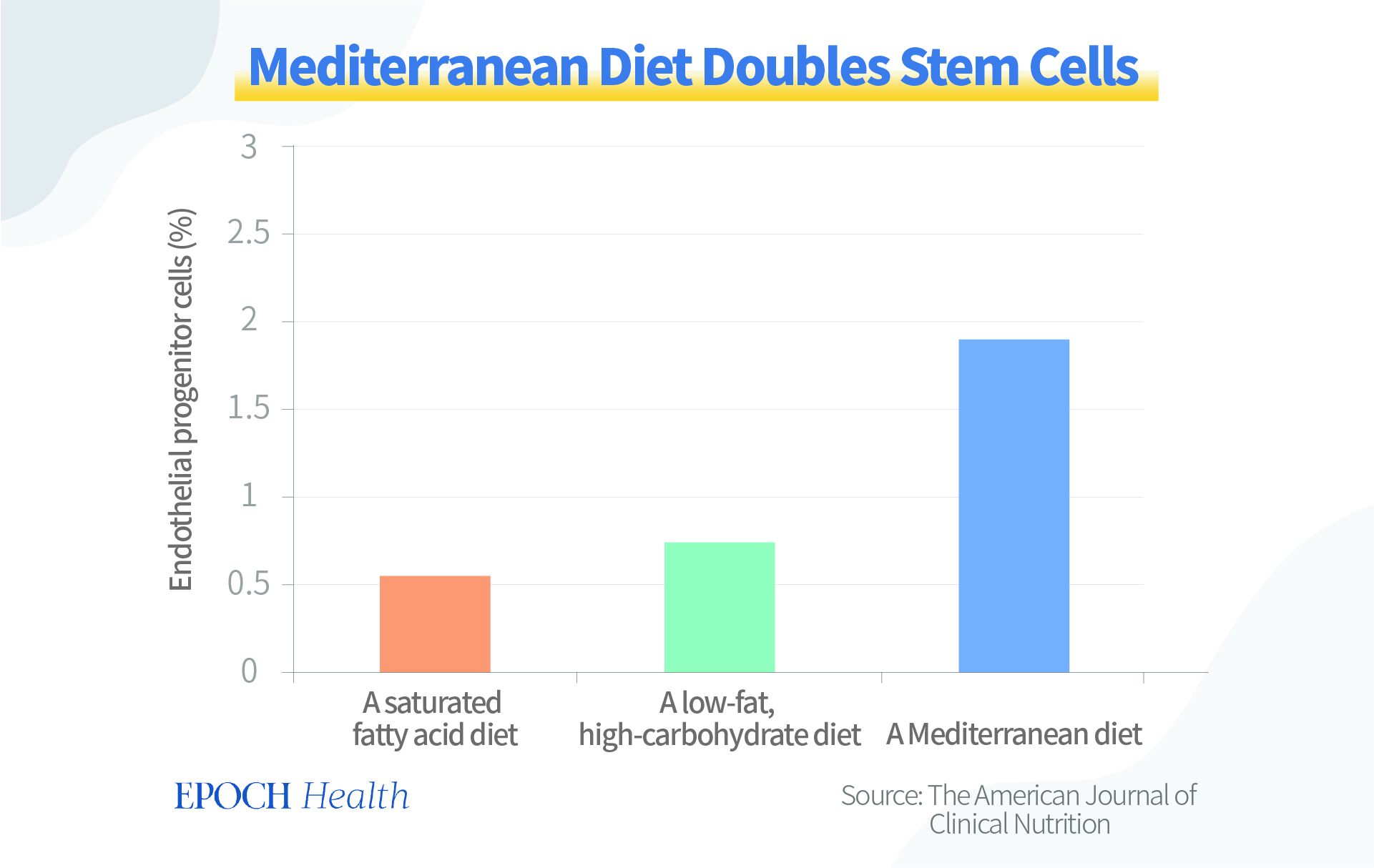
A Mediterranean diet rich in virgin olive oil is effective in boosting stem cells. A 4-week control study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2011) showed that compared to those on a diet high in saturated fat or a diet low in fat but high in carbohydrates, those on a Mediterranean diet rich in virgin olive oil showed a significant doubling in their endothelial progenitor cell count in the blood.
2. Dark chocolate
Dark chocolate contains flavanols that have biological properties. Researchers at the University of California recruited patients with coronary artery disease in a 30-day controlled trial. One group drank hot chocolate low in flavanols (only nine mg per serving) twice a day, and the other group drank hot chocolate high in flavanols (containing 375 mg per serving) twice a day. The results were surprising: the group with high-level flavanol had twice as many stem cells in their blood as that with low-level flavanol, and the former’s blood flow improved twice as much as the latter.
3. Black tea
A team of Italian researchers divided patients who had mild to moderate hypertension but did not receive medication into two groups. Group A drank plain black tea without sugar and milk twice a day while group B drank other beverages twice a day. One week later, blood tests showed the number of endothelial progenitor cells in the blood in the black-tea group rose by 56 percent, with an improved ability of blood vessel widening.
Best Stem Cell Supplements
Can stem cells be increased or enhanced via supplements that could be considered more affordable than a $20,000 syringe of placental, amniotic, umbilical, fat- or bone-derived stem cells?So, if you plan to naturally boost stem cell regeneration via supplements, below are some of the top science backed supplements that you need to consider.
1. Glucosamine and Chondroitin
Glucosamine has been associated with reduced mortality in humans (R,R), and can extend lifespan in animals (R,R).
Glucosamine can for example help mesenchymal stem cells to generate cartilage cells (R). Glucosamine can also improve stem cell proliferation in the gut (R,R). These two supplements are commonly used in arthritis treatments and are often derived from shellfish. Hence it makes sense that glucosamine can promote MSCs (Mesenchymal Stem Cells) to become cartilage and inhibit the breakdown of cartilage. Chondroitin can also enhance the ability of MSCs to turn into cartilage (R).
Chondroitin also has real measurable effects on knee cartilage in actual patients. In one study, it reduced cartilage volume loss on MRI after 6 months (R). Glucosamine also seemed to help cartilage quality when measured on a specialized MRI (R). In another study, glucosamine reduced cartilage breakdown products (R). Finally, when compared to prescription Celebrex, the combination of glucosamine and chondroitin were better at improving function and reducing cartilage breakdown in the knee (R).
Glucosamine can for example help mesenchymal stem cells to generate cartilage cells (R). Glucosamine can also improve stem cell proliferation in the gut (R,R).
Chondroitin also has real measurable effects on knee cartilage in actual patients. In one study, it reduced cartilage volume loss on MRI after 6 months (R). Glucosamine also seemed to help cartilage quality when measured on a specialized MRI (R). In another study, glucosamine reduced cartilage breakdown products (R). Finally, when compared to prescription Celebrex, the combination of glucosamine and chondroitin were better at improving function and reducing cartilage breakdown in the knee (R).
2. Curcumin (Turmeric)
The most commonly promoted anti-inflammatory supplements right now are curcumin and turmeric. Turmeric and curcumin are derived from the turmeric root with turmeric being the spice you know from Indian cooking, and curcumin one of the chemical compounds known as curcuminoids, which are believed to be biologically active. In addition, in order for curcumin to be absorbed in the gut, a black pepper extract is commonly required.
In one study that used adipose MSCs to treat heart attacks, curcumin improved the viability of the cells, reduced scarring in the heart muscle being repaired, and promoted new blood vessel formation (R). In another involving bone marrow MSCs, curcumin improved bone formation (R).
The curcuminoids also impact arthritis through anti-inflammatory pathways and reducing inflammatory cytokines. All of these effects have translated into real measurable impacts on patients with knee arthritis (R). In other studies, Curcumin has been shown to be as effective as common NSAID anti-inflammatories such as Diclofenac (R).
By itself, curcumin is poorly absorbed. Among the methods devised to address the issue, the most common (and most often tested) is to pair curcumin with piperine (a black pepper extract).
To supplement curcumin with piperine, take 500 mg of the former with 5-6.7 mg of the latter, thrice a day (i.e., 1,500 mg of curcumin and 15-20 mg of piperine per day) (R).
In one study that used adipose MSCs to treat heart attacks, curcumin improved the viability of the cells, reduced scarring in the heart muscle being repaired, and promoted new blood vessel formation (R). In another involving bone marrow MSCs, curcumin improved bone formation (R).
The curcuminoids also impact arthritis through anti-inflammatory pathways and reducing inflammatory cytokines. All of these effects have translated into real measurable impacts on patients with knee arthritis (R). In other studies, Curcumin has been shown to be as effective as common NSAID anti-inflammatories such as Diclofenac (R).
To supplement curcumin with piperine, take 500 mg of the former with 5-6.7 mg of the latter, thrice a day (i.e., 1,500 mg of curcumin and 15-20 mg of piperine per day) (R).
3. Resveratrol and Pterostilbene
Resveratrol (RSVL) is a natural type of polyphenolic phytoestrogen and is mainly found in red grapes, blueberries, peanuts, and other plants. The effect of resveratrol on stem cell is well documented (R).
It also helps MSC (mesenchymal stem cell) differentiation into osteogenic (bone related) cells and suppresses differentiation into the fat related tissue lineage [R].
The combination therapy of MSCs (mesenchymal stem cell) transplantation and resveratrol has also played a great therapeutic effect in animal models of diabetic complications (R, R, R).
According to Examine.com:
- The lower end of supplementation tends to be for cardiovascular health, insulin sensitivity, and longevity for somebody who is otherwise unhealthy is 5-10mg daily. For persons who are otherwise healthy, dosages between the range of 150-445mg have been used (with no clear indication for what is the optimal dose).
- Supplementing for cerebral blood flow requires a dose in the 250-500mg range whereas supplementation for aromatase inhibition requires 500mg as well.
- Supplementation of resveratrol refers to trans-resveratrol exclusively.
- The lower end of supplementation tends to be for cardiovascular health, insulin sensitivity, and longevity for somebody who is otherwise unhealthy is 5-10mg daily. For persons who are otherwise healthy, dosages between the range of 150-445mg have been used (with no clear indication for what is the optimal dose).
- Supplementing for cerebral blood flow requires a dose in the 250-500mg range whereas supplementation for aromatase inhibition requires 500mg as well.
- Supplementation of resveratrol refers to trans-resveratrol exclusively.
4. Quercetin and Fisetin
This can be found in many fruits, vegetables, grains, and leaves. Kale and red onions are examples of foods that contains an appreciable amount of quercetin among many others. It comes with a bitter flavor and is commonly used as an ingredient in foods, beverages, and dietary supplements.
Here are the benefits of quercetin: - Antioxidant
- It supports mitochondria
- It can prevent the death of cells
- It can protect your body by reducing your stress levels
- It can serve as a natural antihistamine and can get rid of allergy symptoms
- It is a safe alternative to painkillers since it can treat arthritis and joint pain
- Research suggests that it can support stem cell growth and differentiation (R)
The recommended dosage for quercetin: - Currently, there are no ideal amounts set by the scientific community. You can ask your doctor regarding this one to find out how much is needed based on your health's current status.
- Majority of supplements require 500mg and it has to be taken twice daily. But with quercetin, you can already experience the benefits even if you take something lesser than that considering that it's known to be diet rich.
According to Examine.com:- Dosages of quercetin used are in the range of 12.5 to 25mg per kg body weight, which translates to a range of 1,136-2,272mg daily consumption of quercetin when in isolation.
- It is suggested to supplement with other bioflavonoids such as resveratrol, genistein, or green tea catechins to increase the potency synergistically and theoretically get the benefits at a reduced level of intake.
- When looking for quercetin, the form of dihydrate has the apparent best bioavailability followed by glycosides, aglycone, and finally rutinoside.
Fisetin is a molecular cousin to quercetin. Fisetin is a naturally occurring substance found in fruits and vegetables, such as strawberries, apples, grapes, onions, and cucumbers.
Here are the benefits of quercetin:
- Antioxidant
- It supports mitochondria
- It can prevent the death of cells
- It can protect your body by reducing your stress levels
- It can serve as a natural antihistamine and can get rid of allergy symptoms
- It is a safe alternative to painkillers since it can treat arthritis and joint pain
- Research suggests that it can support stem cell growth and differentiation (R)
- Currently, there are no ideal amounts set by the scientific community. You can ask your doctor regarding this one to find out how much is needed based on your health's current status.
- Majority of supplements require 500mg and it has to be taken twice daily. But with quercetin, you can already experience the benefits even if you take something lesser than that considering that it's known to be diet rich.
- Dosages of quercetin used are in the range of 12.5 to 25mg per kg body weight, which translates to a range of 1,136-2,272mg daily consumption of quercetin when in isolation.
- It is suggested to supplement with other bioflavonoids such as resveratrol, genistein, or green tea catechins to increase the potency synergistically and theoretically get the benefits at a reduced level of intake.
- When looking for quercetin, the form of dihydrate has the apparent best bioavailability followed by glycosides, aglycone, and finally rutinoside.
5. NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide)
NMN is a substance that increases NAD levels in our cells. NAD is a pivotal molecule to protect and repair DNA and the epigenome, including in stem cells.
NMN can improve and protect stem cells such as mesenchymal stem cells that form bone and fat tissue (R,R).
Researchers from the East China University of Science and Technology in China show that nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) — an NAD+ precursor known to elevate NAD+ levels — helps to maintain the functional longevity of stem cells in a dish, which can lead to improved effectiveness of stem cell therapies. As published in Antioxidants (2023), Zheng and colleagues report that NMN enhances stem cell migration, diminishes stem cell ROS, and prevents stem cell senescence.
NMN can improve and protect stem cells such as mesenchymal stem cells that form bone and fat tissue (R,R).
6. Vitamin C and AKG (Alpha KetoGlutarate)
7. Glycine (Amino Acid)
Glycine is a naturally-occuring substance in our body; in fact, it’s an amino acid. However, during aging, levels of glycine decline.
Glycine has shown to improve stem cell health (R,R). It can do this by protecting proteins in cells, or by inducing autophagy, which is the digestion of cellular waste.
Glycine has shown to improve stem cell health (R,R). It can do this by protecting proteins in cells, or by inducing autophagy, which is the digestion of cellular waste.
8. Green Tea Extract
9. Molecular Hydrogen
Molecular hydrogen is the smallest anti-oxidant. The ability of molecular hydrogen (H2) to protect the DNA and the mitochondria from oxidative damage may have beneficial effects on chronic diseases and cancer. But perhaps it could help slow down or reverse the aging process itself. A couple of cellular studies give us some interesting clues [R, R].
It was already discovered that hydrogen can prolong the life of stem cells by reducing oxidative stress
(Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010).
A hydrogen-rich environment reduced both oxidative stress and aging in cells. Some scientists think
that drinking hydrogen water could increase longevity in humans (Circ J. 2016).
It was already discovered that hydrogen can prolong the life of stem cells by reducing oxidative stress
(Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010).
A hydrogen-rich environment reduced both oxidative stress and aging in cells. Some scientists think
that drinking hydrogen water could increase longevity in humans (Circ J. 2016).
10. L-Carnosine (Amino Acid)
L-Carnosine is a “performance enhancer” amino acid shown to enhance muscular endurance. In fact, many who take this potent ingredient report being able to dramatically increase strength performance at the gym, as well as:
11. Leucine (Amino Acid)
12. Taurine
Stem cells hold the key to tissue repair and regeneration. But as the body ages, its numbers and activity decline.
Studies have shown that taurine can help stimulate stem cell production (Nutr Neurosci 2017), particularly neural stem cells, which can boost brain function, in addition to regenerating various tissues throughout the body.
Studies have shown that taurine can help stimulate stem cell production (Nutr Neurosci 2017), particularly neural stem cells, which can boost brain function, in addition to regenerating various tissues throughout the body.


Comments
Post a Comment